CHAPTER 7 : STORING ORGANIZATIONAL INFORMATION-DATABASES
Database - maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees), and places (warehouses).
Hierarchical database model - information is organized into a tree-like structure that allows repeating information using parent/child relationships in such a way that it cannot have too many relationships.
Network database model - is a flexible way of representing objects and their relationships.
Relational database model - type of database that stores information in the form of logically related two-dimensional tables.
This picture below show the hierarchical, network and relational structure :-
ENTITIES AND ATTRIBUTES
entity - the relational database ,model is a person, place, thing model is a person, place, thing, transaction, or event about which information is stored.
attributes - fields or columns, are characteristics or properties of an entity class.
KEYS AND ATTRIBUTES
primary key - group and fields that uniquely identifies a given entity in a table.
foreign key - the relational database model is a primary key of one table that appears as an attribute in another table and acts to provide a logical relationship between two tables.
RELATIONAL DATABASE ADVANTAGES
-Increased flexibility
-Increased scalability and performance
-Reduced information redundancy
-Increased information integrity (quality)
-Increased information security
#INCREASED FLEXIBILITY
Databases tend to mirror business structures and a good database can handle changes quickly and easily.
physical view - information deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device such as a hard disc.
logical view - information focuses on how users logically access information to meet their particular business needs.
#INCREASED SCALABILITY AND PERFORMANCE
scalability - how well a system can adapt to increased demands.
performance - how quickly system performs a certain process or transaction.
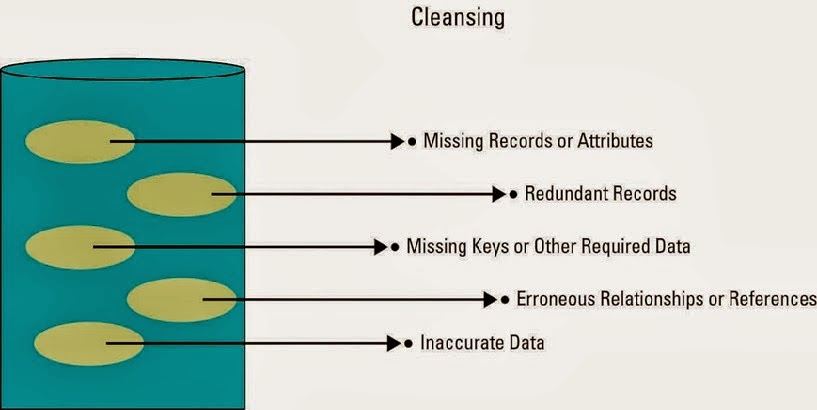
#REDUCED INFORMATION REDUNDANCY
redundancy - duplication of information, or storing the same information in multiple places.
#INCREASED INFORMATION INTEGRITY (QUALITY)
information integrity - measure of the quality of information.
relational integrity constraints - rules that enforce basic and fundamental information- based constraints.
business-critical integrity constraints - enforce business rules vital to an organization's success an often require more insight and knowledge than relational integrity constraints.
#BUSINESS INFORMATION SECURITY
any asset that the organization must protect its information from unauthorized users or misuse.
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (DBMS)
-software through which users and application programs interact with a database.
DATA DRIVEN WEBSITE
-interactive website kept constantly updated and relevant to the needs of its customers through the use of a database.
INTEGRATING INFORMATION AMONG MULTIPLE DATABASES
integration - allows separate systems to communicate directly with each other.
forward integration - takes information entered into a given system and sends it automatically to all downstream systems and processes.
backward integration - takes information entered into a given systems and sends it automatically to all upstream systems and processes.

























.png)